7 Different Types of 3D Rendering Techniques Used by Professionals

3D rendering is a wonderful blend of technicality with creativity and is a unique work of art. For the most popular and desirable Hollywood feature films, animated movies, video games, etc., - high-end 3D rendering is the key to their enormous success.
Curious about the different 3D rendering techniques used in the industry? Give this blog a read!
What Are the Different Types of 3D Rendering Methods?
Based on the requirements and applications of the renders, 3D rendering artists deploy the techniques.
Then comes the role of digital lighting techniques that gives an evenly-balanced light and shadow.
Mainly, rendering techniques are used to replicate how a light source hits an object in the real world. This is the key to producing a compellingly rendered image.
-
Rasterization
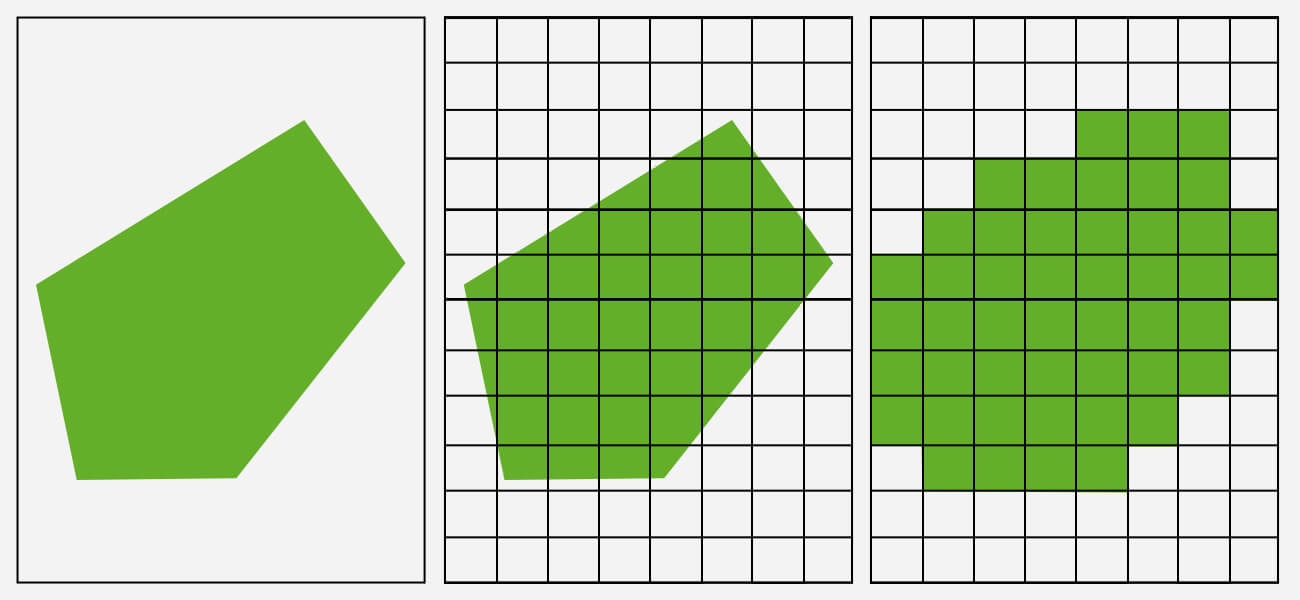 Rasterization technique
Rasterization techniqueThe rasterization method is a widely used and quicker rendering technique than any of its other counterparts. Here, the model is treated as a polygon mesh, which is a collection of vertices.
Each of these vertices is attached to a unique set of texture and color codes that the texturing software extracts and uses to fill the particular areas with their respective colors and textures.
Usually, for real-time rendering of video games and AR/VR simulations, rendering experts use this technique.
-
Ray-Casting
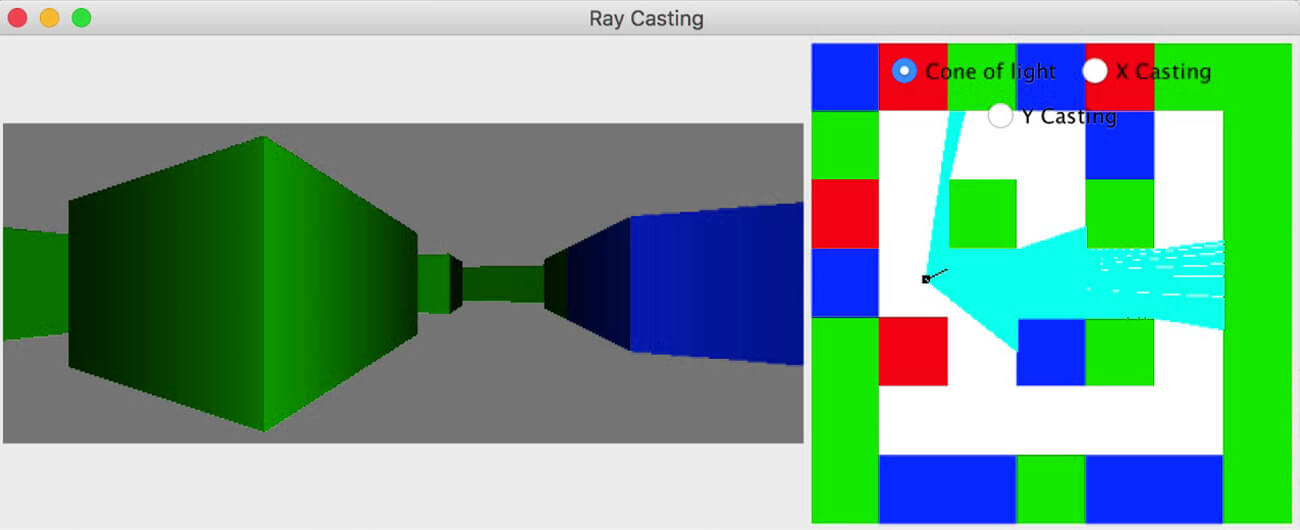 Ray Casting technique
Ray Casting techniqueRay casting is a fantastic technique that helps the artist correctly place the light sources within the 3D environment. It is fast, accurate, and gives a highly lifelike appearance to the textures, lights, and colors added to the models.
Ray casting is done by casting rays directly on the 3D model and transforming the data and geometric information into a 3D projection.
-
Ray-Tracing
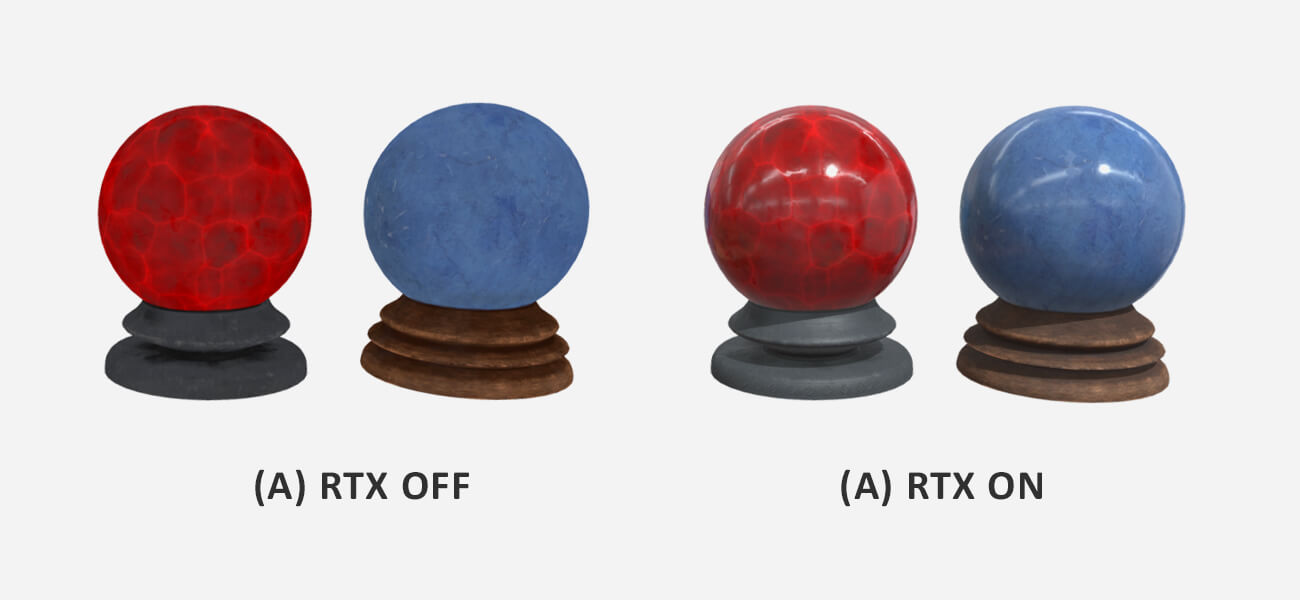 Ray tracing technique
Ray tracing techniqueRay tracing is another terrific method of rendering that simulates reflections, shadows, and refractions of the light, depicting the light source better than the ray casting technique. The primary rays from the camera are cast onto the 3D model to create secondary rays.
Based on the object or model’s surface, the reflection, refraction, and shadow rays are emitted. It is a comparatively slower process than ray casting but produces an accurate lighting effect on the eyes, making the model look hyper-realistic.
-
Interactive-Rendering
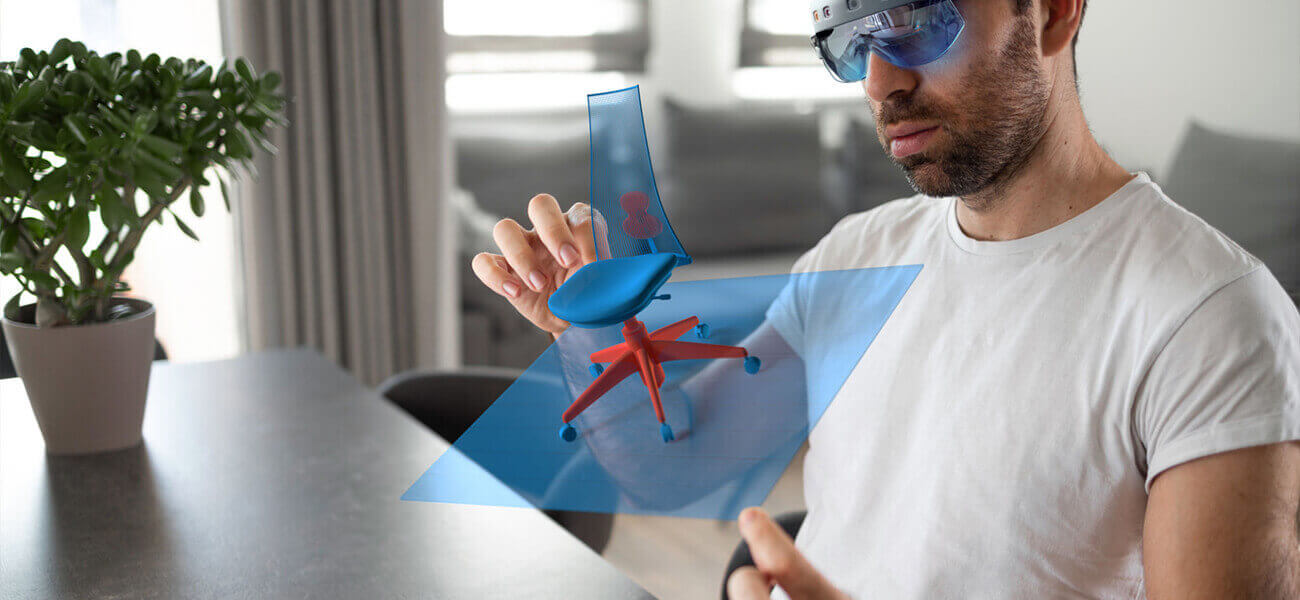 Interactive rendering
Interactive renderingJust like the rasterization technique, this technique is also widely used for gaming and interactive graphics, where real-time information exchange happens, and images are processed from 3D information at a significantly higher speed.
-
Scanline Rendering
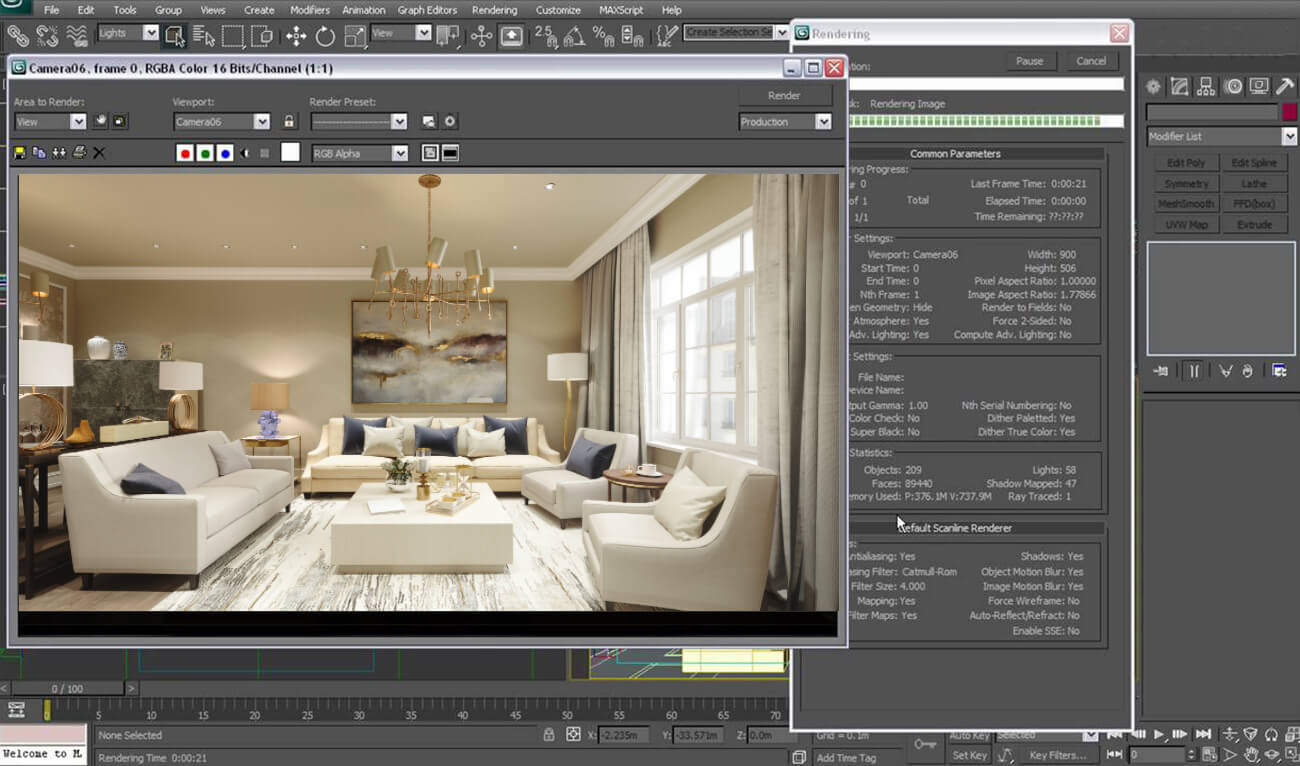 Scanline rendering
Scanline renderingThis is the best go-to technique for a renderer when the rendering time needs to be reduced. Unlike any other rendering technique, scanline rendering implements a real-time rendering based on a polygon-by-polygon basis (usually common in 3D modeling ) instead of a pixel-by-pixel rendering process.
The scanline rendering achieves 60 fps (frames per second) speed when used with multiple lighting setups facilitated by pre-computed lighting in the software.
-
Rendering Equation
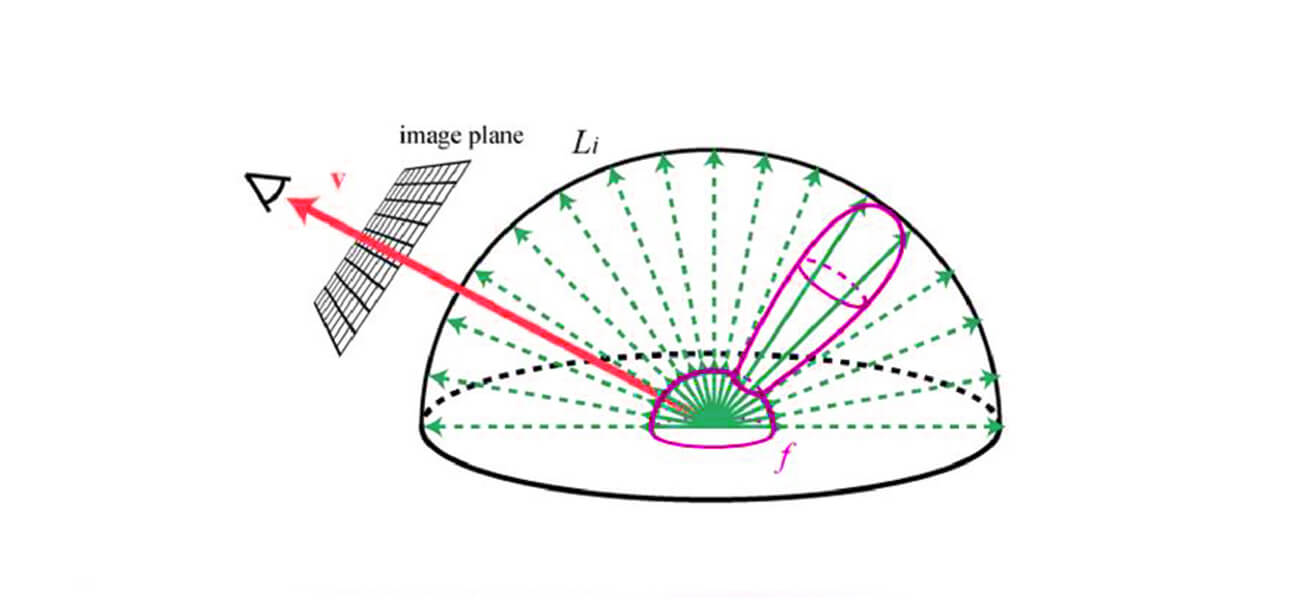 Rendering equation
Rendering equationThis technique is the product of the latest advancements in 3D rendering and works on an equation depicting light emission from multiple sources.
In simple terms, the rendering equation technique considers all the light sources in the render from whichever surfaces they radiate and bounce off instead of only the direct illumination. This majorly helps the 3D designer to create highly realistic three-dimensional scenes.
-
Perspective Projection
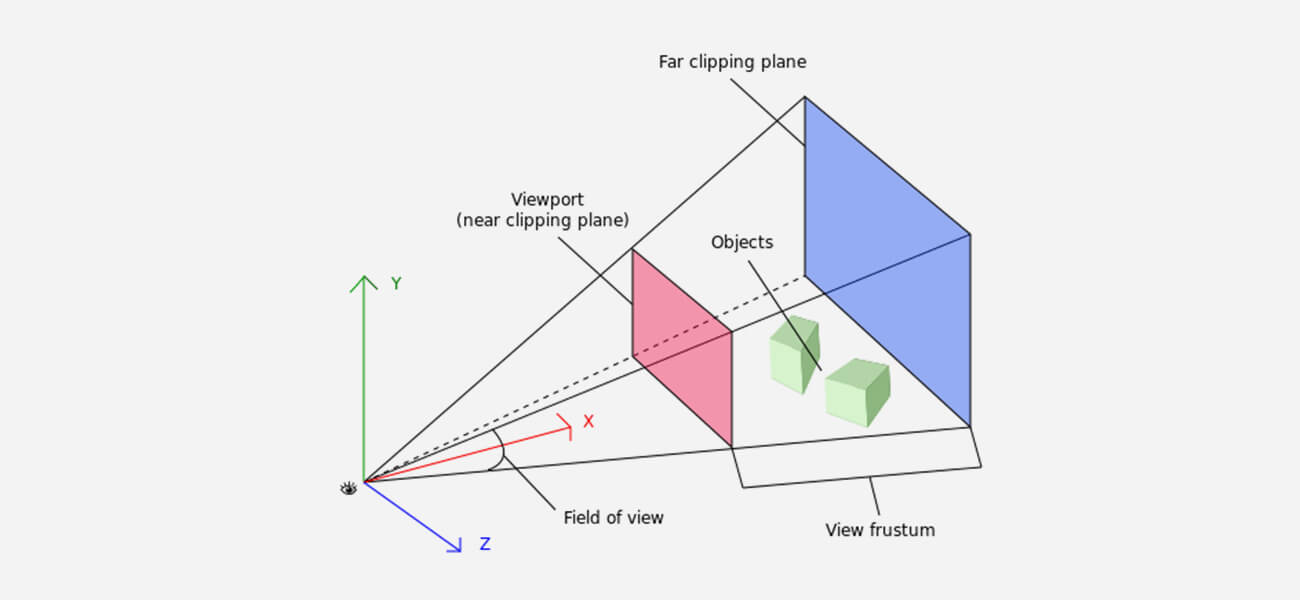 Perspective projection
Perspective projectionThis technique gives a perspective or an idea of the distance between the object and the viewer’s eyes. It accurately replicates how we see the world around us by making far-away objects smaller and nearer objects bigger.
3D rendering programs multiply a “dilation constant” that gives the objects a precise distance compared to the required size within the 3D scene or environment. Thus, the illusion of perspective is generated.
Pro Tip: Optimize your Image Render Resolution
Resolution optimization is a step essentially required for a high-resolution and realistically rendered image.
Resolution depends upon the pixel density of an image, I.e., the number of pixels used to create the image. The denser and higher number of pixels (pixels per inch), the clearer the rendered image will be.
With the passage of time and the advancement of 3D technology, it has gained worldwide popularity and acceptance in a variety of fields.
From healthcare and scientific research to the advertisement, eCommerce, public relations, and the fashion industry - we can see the effects of 3D-rendered photorealistic images everywhere. The reason behind this intense usage of 3D rendering is that it can impress, attract, inform, and win over the audience in the most desirable manner.
So, if you are a marketer finding ways to carve a niche for yourself, get in touch with Top 3D visualization firms with years of experience and expertise who can help you convey complex visual information in a clear, visually appealing, and easy-to-understand manner. Leverage the potential of 3D rendering solutions today and stand out in the crowd!
Contact Us

